Point-based Point Cloud Neural Networks (PCNNs) have attracted much attention for their higher accuracy than voxel-based and multi-view-based PCNNs. Nevertheless, the increasing scale of point cloud data poses a challenge for real-time processing. Numerous previous works focus on accelerating PCNN inference but only optimize specific stages, limiting their generality to different networks with diverse performance bottlenecks.
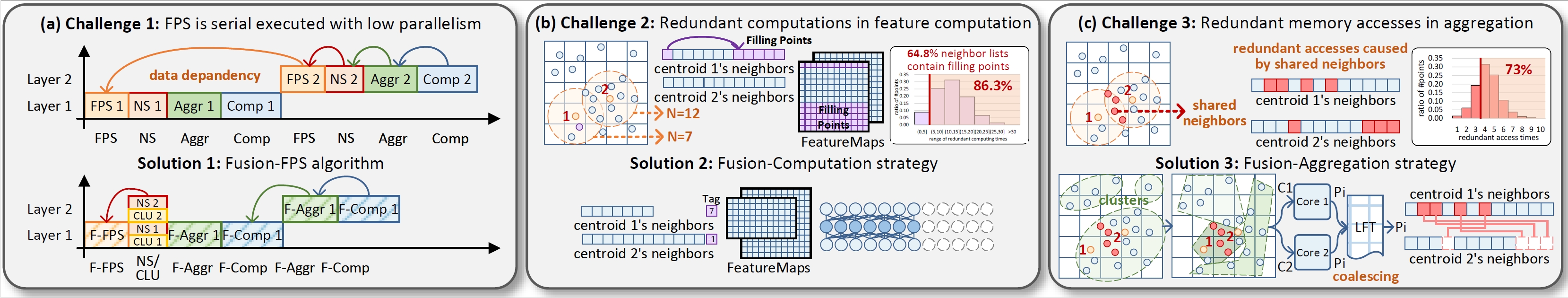
In this paper, we take nearly all stages of PCNNs into account, and propose 3 orthogonal algorithms, including Fusion-FPS, Fusion-Computation, and Fusion-Aggregation. We introduce Fusion-FPS to alter the sequential execution flow by reducing the Farthest Point Sampling (FPS) across layers to once and organize all neighbor search stages in parallel. To exclude redundant feature computations of “Filling Points”, we propose Fusion-Computation, identifying the presence and locations of “Filling Points” and directly borrowing the nearest neighbor features for them. To eliminate redundant memory accesses caused by shared neighbors in aggregation, we present Fusion-Aggregation, which clusters nearby centroids and coalesces their replicated accesses. In support of our algorithms, we co-design FusionArch, an architecture that implements our strategies and further optimizes memory access via a Local Fusion-Aggregation Table (LFT). We evaluate FusionArch on both server-level and edge-level platforms on 5 PCNNs across 4 applications and show remarkable accuracy and performance gains. On average, FusionArch achieves 2.6x, 5.6x, 13.0x speedup and 17x, 22x, 62.4x energy savings over PointAcc.Server, NVIDIA A100 GPU and Intel Xeon CPU, respectively. Moreover, it outperforms PRADA, PointAcc.Edge, Mesorasi and GPU with speedups of 2.4x, 2.9x, 5.3x, 5.5x, and energy savings of 4.4x, 7.2x, 12.4x, 11.5x, respectively.
Authors: Xueyuan Liu, Zhuoran Song, Guohao Dai, Gang Li, Can Xiao, Yan Xiang, Dehui Kong, Ke Xu and Xiaoyao Liang